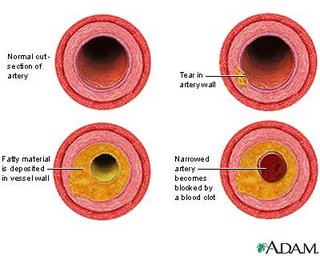
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which fatty material collects along the walls of arteries. This fatty material thickens, hardens, and may eventually block the arteries.
Atherosclerosis is a common disorder of the arteries. It occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries and form hard substances called plaque.
Eventually, the plaque deposits can make the artery less flexible. This makes it harder for blood to flow. If blood flow in the arteries leading to the heart is reduces, chest pain can occur. Plaques can also break apart, causing pieces of material to move through the artery. This is a common cause of heart attack and stroke. Blood clots can also form around the plaque deposits. Clots block blood flow. If the clot moves into the heart, lungs, or brain, it can cause a stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism.
Risk factor:
Smoking
Diabetes
Obesity
High blood pressure
High-fat diet
Personal or family history of heart disease
Diabetes
Obesity
High blood pressure
High-fat diet
Personal or family history of heart disease
Symptom.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis are usually not seen until blood flow becomes slowed or blocked.
Typical symptoms of atherosclerosis include chest pain if an artery to the heart is involved.
or leg pain when a leg artery is involved. Sometimes symptoms occur only with activity. In some people, however, they may occur at rest.
Typical symptoms of atherosclerosis include chest pain if an artery to the heart is involved.
or leg pain when a leg artery is involved. Sometimes symptoms occur only with activity. In some people, however, they may occur at rest.
Complications:
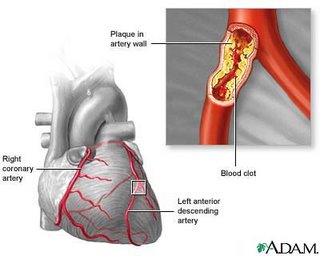
Coronary Artery disease--
the blood supply to the heart is insufficient due to atherosclerosis/plaque in the arteries to the heart; a symptom is angina (chest pain)
Heart attack
TIA (Transient Ischaemic Attack) or Stroke--
Insufficient blood supply to the limbs (mainly the legs and feet) due to obstruction (claudication)
Damage to organ
Damage to organ
Atherosclerosis and obstruction of bypass grafts


No comments:
Post a Comment